Table of Contents
Imagine a heating and cooling system that not only keeps you comfortable year-round but also helps protect the environment and saves you money on utility bills. Meet the heat pump, a versatile and energy-efficient technology that has gained popularity as the most sustainable solution for modern homes and businesses.
In this article, we will delve into the world of heat pumps, exploring their different types, essential components, operation, winter functionality, installation process, and the many reasons why understanding this technology is crucial in today’s energy-conscious world.
What Are the Different Types of Heat Pumps?
Before we dive into the inner heat pump work, let’s familiarize ourselves with the various types available:
Air-Source Heat Pumps
Air-source heat pumps are the most common type, widely used in both residential and commercial settings. They absorb heat from the surrounding air and transfer it indoors for heating or outdoors for cooling. Their ease of installation and relatively lower upfront costs make them an attractive option for many.
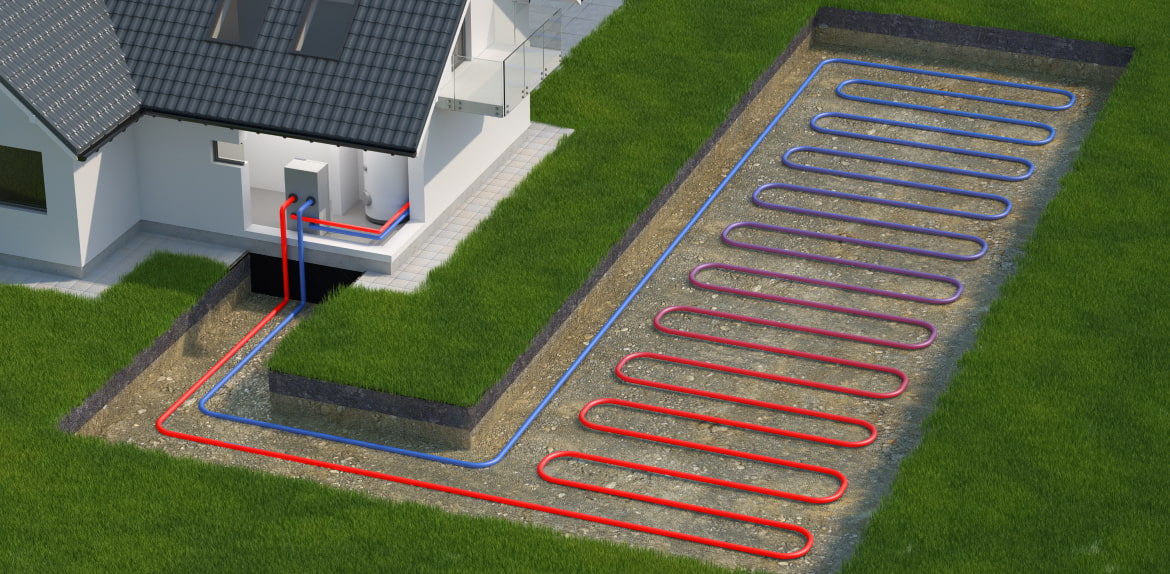
Ground-Source (Geothermal) Heat Pumps
Ground-source heat pumps harness the earth’s constant temperature to provide heating and cooling. By circulating a fluid through underground pipes, they extract heat from the ground during winter and dissipate heat into the ground during summer. While they require more extensive installation and higher initial investments, their efficiency and long-term cost savings are remarkable.
Water-Source Heat Pumps
Water-source heat pumps utilize water bodies such as lakes, rivers, or wells as heat exchange sources. They function similarly to air-source heat pumps but generally offer higher efficiency due to the stable temperatures of water bodies throughout the year. However, access to a nearby water source is essential for their installation.
To make it easier for you to understand the difference between these three types of heat pumps, we’ve prepared a comparative table that allows you to assess all the essential aspects of their performance, efficiency, installation process, maintenance needs, and additional relevant information.
Feature | Air-Source Heat Pump | Ground-Source (Geothermal) Heat Pump | Water-Source Heat Pump |
|---|---|---|---|
Heat Exchange Source | Outdoor Air | Ground | Water Body (Lake, River) |
Efficiency | Good | Excellent | Excellent |
Initial Cost | Low-Moderate | High | High |
Installation Complexity | Low | High | Moderate to High |
Space Requirements | Compact | Significant | Moderate to Significant |
Year-Round Performance | Effective | Consistent | Consistent |
Environmental Impact | Lower Carbon Footprint | Low | Low |
Suitable Locations | All Climates | All Climates | Water Source Proximity |
Heating and Cooling | Yes (Reversible) | Yes (Reversible) | Yes (Reversible) |
Maintenance Needs | Regular | Regular | Regular |
Note that the information in the comparison table may vary depending on specific models, manufacturers, and regional factors.
What Are the Essential Parts of the Heat Pump?
Understanding the essential components of a heat pump is crucial for timely and efficient repairs. Each part plays a vital role in the heat exchange process, ensuring optimum performance. In this section, we will explore the significance of these components and why their proper functioning is essential for your heat pump’s longevity and reliability.
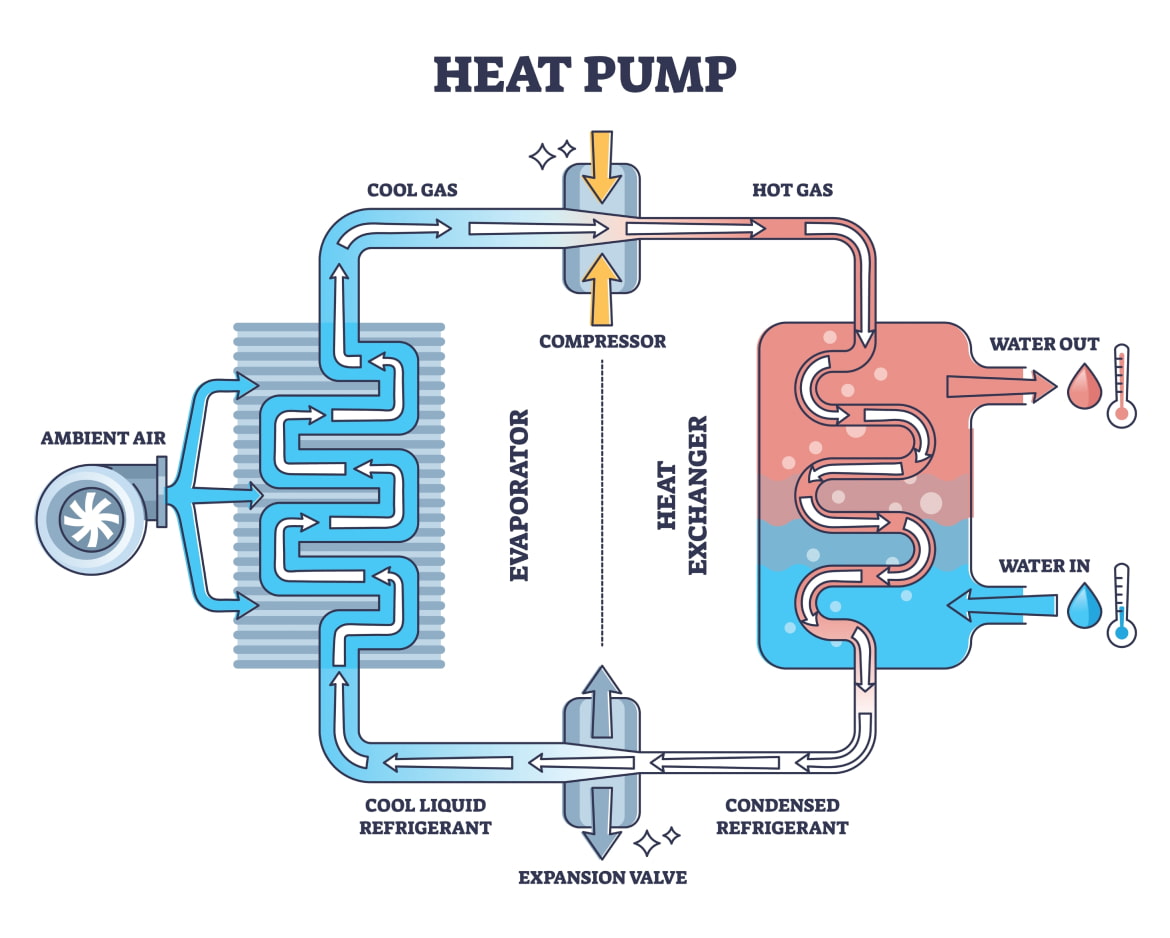
Compressor
The compressor plays a crucial role in the heat pump’s operation. It compresses the low-pressure refrigerant gas, raising its temperature and pressure, making it ready for the heat exchange process.
Condenser
The hot, high-pressure refrigerant gas travels to the condenser, where it releases heat into the indoor environment during heating mode or the outdoor environment during cooling mode. As it cools, the refrigerant transitions into a high-pressure liquid.
Evaporator
In the evaporator, the high-pressure liquid refrigerant expands, turning into a low-pressure gas. This process absorbs heat from the indoor air during cooling mode or the outdoor air during heating mode.
Refrigerant
The refrigerant is the lifeblood of the heat pump, facilitating the transfer of heat between the different components. Modern heat pumps use environmentally friendly refrigerants that have a lower impact on the ozone layer and global warming.
Among all these vital parts, the compressor stands out as the heart of the heat pump, elevating the refrigerant’s temperature and pressure to enable the entire system’s heat exchange process. Due to its central role and intricate mechanics, the compressor is also the most critical and costly part to repair or replace if it malfunctions. Regular maintenance is crucial to keep the compressor functioning optimally and extend the heat pump’s overall lifespan.
Prioritizing scheduled maintenance by qualified technicians can prevent costly breakdowns, ensuring continued efficiency and reliability. Find out more about our maintenance services via the link below, and give your heat pump some love and care.
https://thehvacservice.ca/tune-up/
Now, that you know what is a heat pump and which components of this HVAC unit are the most important, we can skip to the next section of our article.
How Does a Heat Pump Work?
Are you familiar with the process of how does a heat pump work? Meanwhile, understanding the inner workings of a heat pump is not just a matter of curiosity; it holds the key to unlocking the full potential of this remarkable technology. With rising concerns about energy efficiency, environmental impact, and sustainable living, grasping the mechanics behind a heat pump becomes more critical than ever.
In this section, we will delve into the world of heat pump operation, step by step, to shed light on its efficiency, versatility, and how it provides year-round comfort in an environmentally conscious manner.
Step 1: Absorption of Heat (Heating Mode)
In heating mode, the outdoor unit of the heat pump absorbs heat from the surrounding air, even in cold temperatures. The refrigerant within the unit turns into a low-pressure gas as it absorbs heat.
Step 2: Compression and Heat Release
The compressor then takes the low-pressure gas and compresses it, converting it into a high-pressure, high-temperature gas. This heated gas is then pumped to the indoor unit, where it releases heat into the indoor environment through the condenser coil.
Step 3: Distribution of Warm Air
The heat pump’s fan distributes the warm air throughout the living space, providing cozy comfort during chilly days.
Step 4: Reversal for Cooling (Cooling Mode)
During cooling mode, the heat pump reverses the cycle. It absorbs heat from the indoor air and releases it outdoors, effectively cooling the interior space.
We hope that by grasping the fundamental principles of how do heat pumps work, you can gain a deeper appreciation for their capability to harness heat from the surrounding environment and provide year-round comfort while minimizing environmental impact. Whether it’s keeping your home warm during freezing winters or cooling it down in scorching summers, a heat pump’s efficiency directly impacts your comfort and utility costs.
How Does a Heat Pump Work in the Winter?

You might wonder how a heat pump works in the winter, extracting heat from the outside air when it’s freezing outside. The key lies in the heat pump’s ability to maintain efficiency even in low temperatures.
During winter, the outdoor unit’s refrigerant circulates through the heat exchanger, where it absorbs heat from the cold outdoor air. While the air temperature may be chilly, there is still enough heat energy present for the heat pump to operate efficiently. Ground-source heat pumps, on the other hand, tap into the stable temperatures beneath the earth’s surface, ensuring a reliable heat source, no matter how cold it gets outside.
Check out the list of the best heat pump for cold climates in Canada in our previous article via the link below.
https://thehvacservice.ca/best-heat-pump-for-cold-climates-in-canada-rating-list/
As we have explained before, the innovative technology of the heat pump translates to lower energy consumption and reduced utility bills, making heat pumps a cost-effective and eco-friendly solution for year-round comfort. However, in extremely cold climates, air-source heat pumps may experience a slight reduction in efficiency, requiring more energy to extract heat from very cold air. In such cases, ground-source heat pumps with consistent ground temperatures may be a more efficient option.
How to Install a Heat Pump?

Professional installation requires careful planning and an expert understanding of how a heat pump works to ensure optimal system performance. Proper installation is vital for seamless heat exchange and efficient operation. In this section, we will guide you through the step-by-step process.
Step 1: Site Assessment
Qualified HVAC technicians conduct a comprehensive site assessment to determine the most suitable location for the heat pump installation. Factors such as available space, insulation, and proximity to the heat exchange source (air, ground, or water) are carefully evaluated.
Step 2: Choosing the Right Type and Size
Based on the site assessment, the technicians recommend the ideal type and size of the heat pump that aligns with your specific heating and cooling needs. Proper sizing is crucial for ensuring optimal efficiency and comfort.
Step 3: Installation of Indoor and Outdoor Units
With the right equipment and expertise, the technicians proceed to install both the indoor and outdoor units of the heat pump. The indoor unit is typically placed in a utility room or closet, while the outdoor unit is situated outside the property.
Step 4: Commissioning and Testing
Once the installation is complete, the technicians commission and thoroughly test the heat pump to ensure it is operating at peak efficiency. They check for any refrigerant leaks, calibrate the system, and verify its heating and cooling capabilities.
As you can see, the heat pump installation process may not be as easy as it looks. Meanwhile, professional installation of a heat pump is crucial for ensuring optimal system performance and longevity. Only experienced technicians possess the expertise to conduct precise site assessments, selecting the most suitable heat pump type and size for your specific needs.
HVAC Service Solutions takes pride in its Lennox-trained technicians, offering industry-leading expertise for a worry-free installation process. Book an appointment with our HVAC professionals and rest assured that your heat pump operates at its best, providing years of reliable and energy-efficient heating and cooling comfort.
Are you curious about how you can save up to $7800 on your new heat pump unit within Government Heat Pump Rebates Program? Check out our previous article.
https://thehvacservice.ca/government-heat-pump-rebates-in-ontario/
What Is a Heat Pump, and How Does It Work: Conclusion
Heat pumps have revolutionized HVAC, emerging as the sustainable solution for modern homes and businesses. By harnessing heat from the environment, they provide year-round comfort while reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Unlike traditional systems, heat pumps transfer heat, resulting in energy efficiency and lower utility bills. With advancing technology and renewable energy, heat pumps stand as the forefront of eco-friendly heating and cooling.
We hope that by recognizing the significance of each component of the heat pump, especially the compressor, you can prioritize professional installation and regular maintenance and invest in high-quality heat pump systems for long-lasting comfort, energy savings, and environmental benefits.
We remind you that HVAC Service Solutions, with its 30 years of experience and Lennox-trained technicians, ensures expert installation and optimal performance. Embrace the future of sustainability with a heat pump and pave the way for a greener world with HVAC Service Solutions by your side.
Share



















